Are you stressed about your kid’s language abilities? Well, understanding verbs, which form the foundation of every phrase, is a critical component of language acquisition. Verbs provide our thoughts, ideas, actions, meaning, and direction, making them crucial for clear communication.
Children who understand and use a wide variety of verbs can better communicate themselves clearly and efficiently, enabling them to create vivid pictures with their words. We provide a thorough verbs list in this article to assist your youngster in laying a solid foundation for language development.
Whether you’re looking for basic verbs or more sophisticated ones, this extensive list will include all the vocabulary your youngster will need to start speaking.
So let’s embark on this journey of exploring a voyage with a fresh understanding of the importance of verbs.
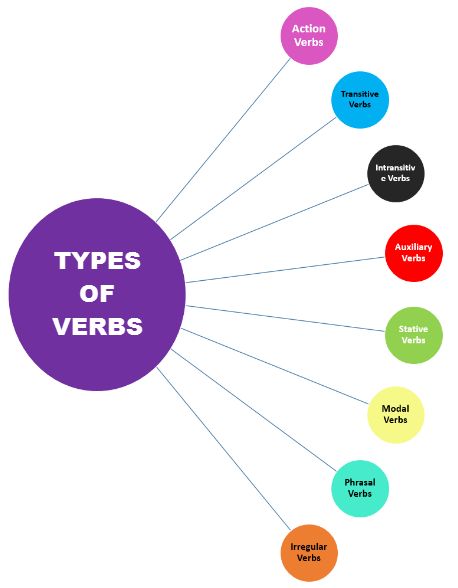
What Are the Different Types of Verbs, and Why Are They Important?
Verbs are an essential language component and represent actions, events, and states in sentences. They are essential for clear communication and are divided into many sorts according to how they are used in sentences. Comprehending the various verb forms is crucial since it makes it easier to construct sentences that make sense and represent various thoughts.
The primary verb categories and their purpose are listed below:
1. Verbs of Action
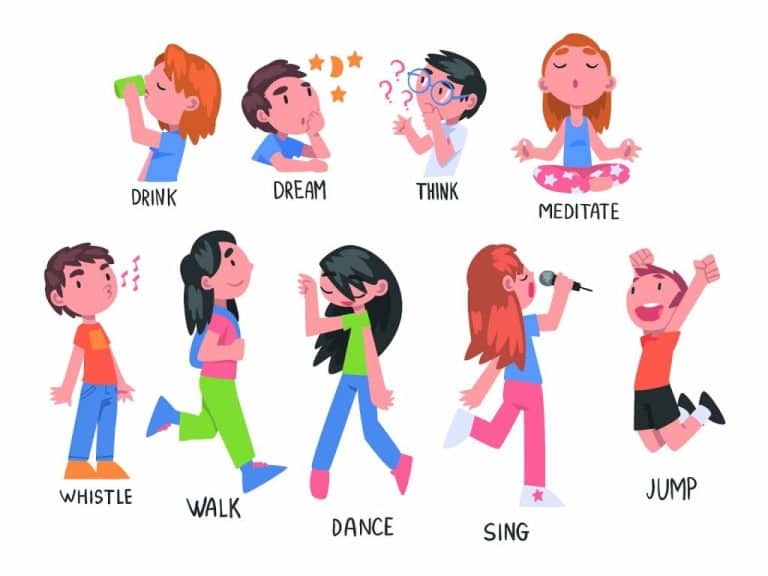
Verbs that express physical or mental actions are called action verbs or dynamic verbs. They give an account of what a subject does or goes through. There are many examples like” jump,” “run,” “sing,” “think,” and “write.” Action verbs give sentences life and motion, which makes them essential for telling stories, expressing activities, and communicating emotions.
2. Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary verbs, also known as helping verbs, are employed in conjunction with main verbs to create a variety of tenses, moods, and voices. Helping verbs include the following “have,” “had,” “has,” “do,” “might,” “must,” etc. Helping verbs are required to express temporal information (past, present, future) and donate opportunities, permissions, and commitments.
3. Copula Verbs
Copula Verbs, also known as linking verbs, link the subject of a phrase to the subject complement, which may be a pronoun, noun, or adjective. Linking verbs, in contrast to action verbs, describe a state or condition rather than showing activity. A few common linking verbs include “is,” “am,” “our,” “was,” etc. We can express qualities and states of being by using linking verbs to connect distinct elements in a sentence.
4. Transitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are action words that need a direct object to convey their meaning fully. They deliver the action directly to the intended recipient. For instance, “ate” is the transitive verb in the sentence. For example, “She ate the cake” and “the cake” are direct objects. Transitive verbs are essential for clear and concise communication because they identify the activity and the intended recipient.
5. Modal Verbs
A particular class of helping verbs known as a modal verb expresses the main verb’s attitude, necessity, possibility, or capacity. The following verbs are examples: “would,” “must,” “can,” “may,” etc. Modal verbs give a statement more nuance by expressing the degree of certainty, willingness, consent, or obligation connected to the action or event.
6. Reflexive Verbs
When the subject acts upon itself, reflexive verbs are used, they are created by finishing the verb with a reflexive pronoun (yourself, myself, him, etc.) For example, “she washed.” Reflexive verbs are required to describe acts where the subject is working against themselves.
7. Intransitive Verbs
Action verbs that do not need a direct object to convey their meaning are known as intransitive verbs. They describe events or acts that do not involve an item. The intransitive verb “sings” is used in the phrase “he sings beautifully,” for example. For expressing acts or situations that stand alone without impacting any object, intransitive verbs are necessary.
It is essential to understand the various kinds of verbs. Each kind of verb has a specific function in human communication, expressing activities, transmitting information, and giving it depth. Verbs are the foundation of efficiently transmitting information and giving it depth. Verbs are the foundation of efficient language use, allowing us to communicate with clarity and accuracy, whether used to describe physical acts, link traits, convey attitudes, indicate time, or exhibit self-action. With verbs, we open up a world full of expression, comprehension, and connection via the art of language, leaving future generations with a permanent legacy of efficient communication.
Why Are Verbs Necessary?
Verbs are essential to communicate. They explain conditions, events, actions, and connections between various aspects. Without verbs, sentences would be meaningless and incoherent, making communication difficult. Children exposed to various verbs early on can better understand and write sentences appropriately expressing their feelings.
Think about the distinction between the words the dog and the dog barked. Using the verb parked, which brings the statement to life with action, helps the listener create a more vivid mental image. Verba enables kids to actively participate in self-expression and storytelling while providing their stories and depth.
Not just this, by exposing your child to this wide variety of verbs, you give your child skills they need to construct sentences that vividly describe experiences, express emotions, and participate in meaningful conversations, laying the groundwork for a lifelong love of language and enhancing their capacity to connect with people deeply.
What is the Major Influence of Vocabulary Growth?
According to research, writing, and other academic areas, expanding one’s vocabulary is a crucial component of language development. Children who have mastered many verbs can better express themselves imaginatively, work through issues, and communicate their emotions.
Your child’s ability to communicate with the world around them improves as their vocabulary grows, which encourages curiosity and desire to learn. Learning a new verb is like opening the door to a new experience; it broadens their perspective on the world and improves their capacity for empathic communication. Furthermore, youngsters with a strong vocabulary can better understand complicated materials, unleashing their potential as lifelong learners.
How to Introduce Verbs to Your Kids
Verb initiation can be a fun and interesting process for your child. The verbs list can be included in various interactive exercises to turn learning into an adventure packed with fun.
Playing interactive verb games like Charades or I Spy, reading aloud from books, engaging in pretend play, and utilizing verb flashcards with detailed visuals are all good ways to encourage your child to appreciate language.
Celebrate each new verb your youngster learns, and use it in amusing situations to promote its use in everyday talks. Including verbs in regular activities may create a language environment that nourishes your child’s linguistic development and fosters their natural curiosity to learn new words.
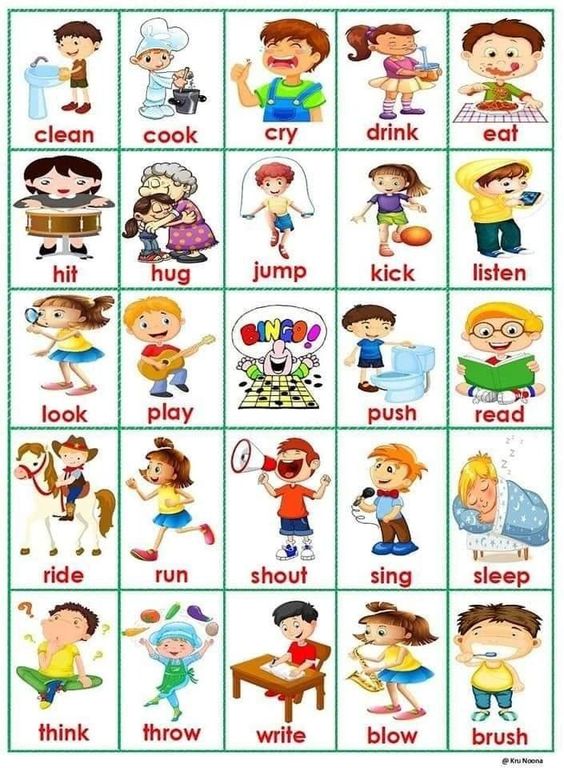
Comprehensive List of Verbs for Kids
The following verb list is comprehensive and includes various action words that kids can learn and incorporate into everyday language. This list includes a wide range of verbs to assist your child in becoming a confident communicator, from basic acts like “eat” and “run” to expressive emotions like “cry” and “laugh.”
Please encourage your child to investigate the meaning of each verb on this list, practice using it in phrases, and even create stories that illustrate the word’s action when they come across each one. Making learning a new language engaging and fun will help students develop a lifelong love of learning. Your child’s language learning journey will be opened up to a world of self-expression and meaningful conversations if you incorporate this complete verbs list into it.
The foundation for their future academic achievement and personal development is laid by foresting their verb vocabulary, enabling them to succeed as self-assured and eloquent people. So let’s start this thrilling journey of language exploration together and watch as our kids develop into articulate storytellers and perspective observers of their surroundings.
List of verbs –
- Run, Jump, Dance, Read, Write, Eat, Sleep, Laugh
- Cry, Smile, Play, Learn, Talk, Listen, Watch, Cook
- Draw, Paint, Clap, Skip, Hop, Swim, Ride, Build
- Fly, Plant, Water, Dig, Catch, Throw, Kick, Hug
- Kiss, Share, Help, Clean, Wash, Brush, Hide
- Seek, Count, Think, Imagine, Dream, Explore
- Solve, Create, Grow, Shout, Whisper, Beg
- Apologize, Climb, Crawl, Hop, Skip, March
- Sneak, Bounce, Balance, Tumble, Slide, Spin
- Drive, Fix, Listen, Speak, Sing, Roar, Bark, Meow
- Buzz, Moo, Quack, Swim, Fly, Crawl, Swing
- Dance, Skip, Tip-Toe, Prance, Bow, Wave
- Point, Spin, Blink, Wink, Nod, Shake, Surprise
- Stretch, Yawn, Giggle, Sigh, Frown, Worry
Expand Your Language Proficiency with Additional Verbs
1. Fundamental Verbs
Once your child is familiar with the list of fundamental verbs, supporting continued language development is crucial. Gradually introduce verb tenses, phrasal verbs, and more sophisticated verbs to improve their language skills. This verb expansion journey may include verbs like “persuade,” “analyze,” “venture,” etc. So let’s have a look at the verbs list –
- Somersault, Sprint, Croon, Analyze, Embark
- Sculpt, Whistle, Marvel, Coax, Persuade
- Migrate, Assemble, Imagine, Meditate, Devour
- Fabricate, Illuminate, Disguise, Grumble
- Conquer, Unravel, Inquire, Simmer, Merge
- Flourish, Commence, Shimmer, Traverse
2. Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal Verbs, verbs followed by one or more particles, give communication additional nuance and depth. We can tell engaging stories, communicate our sentiments precisely, and articulate our ideas clearly with a solid command of verb tenses. Explore some of the common phrasal verbs with your child that are given below –
- View Up, Leave Now, Activate, Pick Up
- Broken down, Settle in, Give up, Put on
- Cut off, Run out of, Get up, Look for
- Catch up, Go over, Look forward to
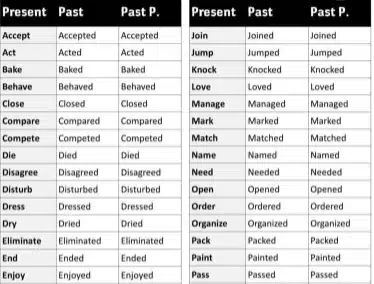
3. Past Tense Verbs
Past tense verbs for your child’s vocabulary help them develop a sense of time. Your child can better describe past events and experiences if they comprehend how to use the past tense. So let’s have a look at the verbs list given below-
- Jumped, Ran, Sang, Danced, Read
- Wrote, Ate, Slept, Laughed, Cried
- Smiled, Played, Learned, Talked, Listened
4. Future Tense Verbs
After the Past, teach your child future tense verbs as they anticipate exciting new experiences. Using the future tense encourages youngsters to discuss plans, objectives, and dreams while building a sense of anticipation and aspiration. Now let’s have a look at the list of such verbs given below-
- Will jump, Will run, Will dance, Will Sing
- Will write, Will read, Will eat, Will laugh
- Will sleep, Will cry, Will smile, Will learn
- Will play, Will talk, Will listen, Will hear
Conclusion
All in all, for efficient communication and language mastery, it is crucial to comprehend the various verb tenses. Verbs are building blocks of sentences, giving them the action, meaning, and context necessary to communicate ideas, feelings, and experiences. Action verbs give sentences life by expressing active activities and bringing stories to life.
Linking verbs create links while describing qualities and states of being. Helping verbs is essential in determining a sentence’s tense, mood, and voice and enables us to communicate a variety of possibilities and obligations. Modal verbs provide our language additional nuance by expressing attitudes, potential outcomes, and certainties.
Reflexive verbs are used when the subject takes action on itself or when the subject is acting on itself. We empower ourselves and our kids to create logical and meaningful sentences by applying this understanding of verb kinds to our language learning attempts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Are Verbs Crucial for Language Development Mainly?
Verbs are crucial for language development because they provide our sentence’s movement and meanings. They make communication more effective and interesting by enabling us to express our behaviors, feeling, and state of being. The ability to communicate oneself precisely and creatively is made possible by knowing a variety of verbs, which helps youngsters develop their language skills early on.
How Can I Facilitate My Child’s Acquisition and Retention of The Exhaustive Verbs List?
By including interactive exercises like verb charades, I Spy, and verb flashcards with visual aids as well as verb games, you can make learning verbs easy. Verb usage will also be reinforced by regular dialogues highlighting various acts and emotions.
Are All the Kinds of Verbs the Same?
No, verbs can be divided into many sorts according to how they are used in sentences and what purpose they serve. Action verbs, modal verbs, linking verbs, assisting verbs, transitive verbs, intransitive verbs, and reflective verbs are among the primary categories of verbs. Every verb type has a specific function in language construction.
How Do Modal Verbs Help Sentences Become More Meaningful?
Modal verbs convey the main verb’s attitudes, possibility, necessity, or ability. There are more examples like “could,” “may,” “might,” “shall,” etc. Modal verbs give a statement more nuance by expressing the degree of certainty, consent, willingness, or obligation connected to the action or event.
Why and How Are Auxiliary Verbs Crucial?
Auxiliary verbs, often referred to as helping verbs, are combined with primary verbs to create a variety of tenses, voices, and moods. They must donate possibilities, obligations, and permissions in sentences and express time-related information.